 TSA workflow illustration" width="100%" />
TSA workflow illustration" width="100%" />Tyramide signal amplification (TSA) is a novel technique designed to enhance the detection of low-abundance targets (e.g. proteins and nucleic acid sequences). It can be readily integrated into any application that utilizes horseradish peroxidase (HRP) in its protocol. These applications include ELISA, immunocytochemistry (ICC), immunohistochemistry (IHC) and in situ hybridization (FISH). Advantages of tyramide signal amplification, include:
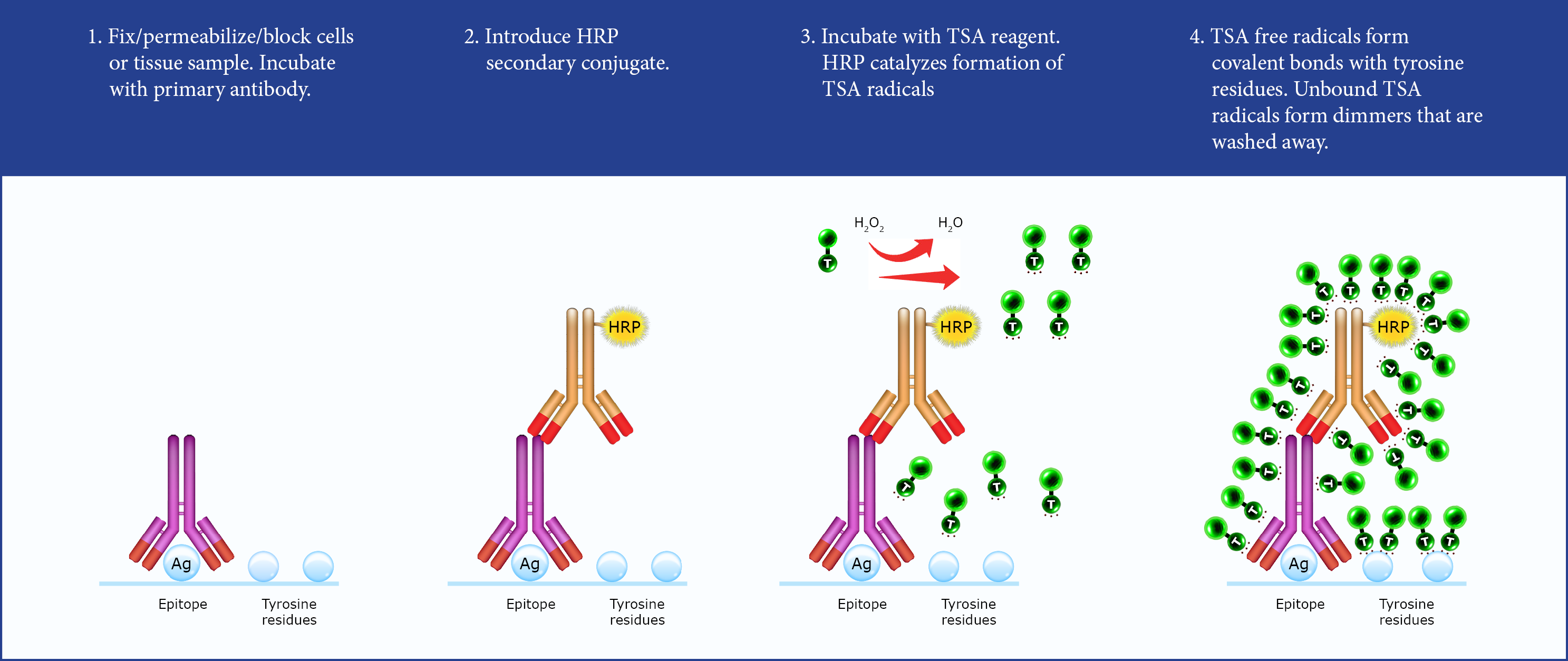
TSA - sometimes called Catalyzed Reporter Deposition or CARD, is an enyzme-mediated detection method that utilizes the catalytic activity of HRP for the covalent deposition of labeled tyramide on and near target proteins or nucleic acid sequences in situ. In the presence of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), HRP converts labeled tyramide substrates into highly-reactive, short-lived tyramide radicals that rapidly bind to tyrosine residues on and proximal to the enzyme site. These labels can be detected by standard chromogenic or fluorescent techniques.
TSA labeling procedure consists of the following steps:
 TSA workflow illustration" width="100%" />
TSA workflow illustration" width="100%" />
Figure 1. Workflow for tyramide signal amplification (TSA). With workflow similar to conventional ICC and IHC methods, TSA can achieve sensitive detection of desired targets in a few simple steps.
| Product Name | Ex/Em (nm) | ε | Φ | Size | Cat# |
| Azido-Cy5 tyramide | 650/669 | 250,000 | 0.27 | 1 mg | 11061 |
| Cy3 tyramide | 554/568 | 150,000 | 0.04 | 1 mg | 11065 |
| Cy5 tyramide | 650/669 | 250,000 | 0.27 | 1 mg | 11066 |
| AF488 tyramide reagent | 499/520 | 73,000 | 0.92 | 200 slides | 11070 |
| AF546 tyramide reagent | 561/572 | 112,000 | 0.1 | 200 slides | 11075 |
| AF594 tyramide reagent | 590/618 | 92,000 | 0.66 | 200 slides | 11082 |
| iFluor® 488 tyramide | 491/516 | 75,000 | 0.9 | 200 slides | 45100 |
| iFluor® 555 Tyramide | 556/569 | 100,000 | 0.64 | 200 Slides | 45105 |
| iFluor® 647 Tyramide | 654/669 | 250,000 | 0.25 | 200 Slides | 45110 |